A rolling scaffolding is a type of supported scaffolding set on wheels. This temporary structure has a base plate integrated with casters or wheels. The overall design allows movement from one place to another conveniently. It has various safety features, including guardrails, locking casters, and toeboards. Another popular name for rolling scaffolds is mobile scaffolds. Workers who need to reposition frequently to perform their tasks make the most of rolling scaffolds, as they boost efficiency and productivity in the work environment.
The main types of rolling scaffolds are Tube and coupler scaffolds, Single bay scaffold towers, mobile towers, Baker style, and Perry style. Rolling scaffolds have many benefits, including mobility, locking mechanisms, reduced dismantling, time efficiency, and versatility. They are also used in building construction, repair and maintenance, window cleaning, window installation, and ceiling repairs.
Table of Contents
What is Rolling Scaffolding?
Rolling scaffolding is a temporary structure mounted on casters or wheels, so moving it from one location to another is possible for workers. Its mobility makes it an ideal framework for all the tasks that need workers to frequently reposition the whole structure, such as plastering, painting, and repairing work on long walls or ceilings. The entire structure is lightweight and easy to assemble, and you can use it for various indoor and outdoor applications. The working platform provides ample space for tools and materials. Rolling scaffolding saves laborers time and energy as they don’t need to repeatedly assemble or disassemble the whole structure. All they need to do is unlock its wheel and move it around, boosting workers’ productivity and letting them complete work quickly and precisely.
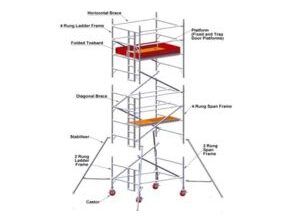
What is the Diagram of Rolling Scaffolding?

Rolling Scaffolding images


What are the Benefits of Rolling Scaffolding?
The eighteen benefits of rolling scaffolding are as follows:
- Design allows movement
- Efficient workplace environment
- Mobility scaffold
- Easy movement
- Enhanced mobility
- Time efficiency
- Versatile applications
- Improved worker safety
- Locking mechanisms
- Safe platform
- Frequent position changes
- Reduced dismantling
- Reassembly
- Increased Safety
- Versatility
- Efficiency
- Space-Saving Design
- Cost-Effective in the Long Run
1. Design Allows Movement
The biggest benefit of rolling scaffolding is its design to integrate wheels or castors, making it a perfect fit for any task that requires movement. There is no need to disassemble it before repositioning it. Unlock its wheel and move it around with ease.
2. Efficient Workplace Environment
Another plus point of rolling scaffolds is that they allow workers to maintain top-notch productivity in the work environment. Adjusting the scaffold’s position is easy, reducing overall downtime.
3. Mobility Scaffold
When a project has a large coverage area and requires efficiency, this mobility scaffold allows the workers to cover large areas without assembling or dismantling the overall structure. All they need to do is unlock its wheels and move it around quickly.
4. Easy Movement
The biggest benefit of mobile scaffolds is their lightweight design, which features casters. Even a single worker can move the whole scaffold around with minimal effort.
5. Enhanced Mobility
Whenever a task requires frequent movement and location changes, such as electrical installation, maintenance, or painting, enhancing the mobility provided by a rolling scaffold is super beneficial.
6. Time Efficiency
The biggest issue with working with a traditional scaffold is that assembly and dismantling are time-consuming. Mobile scaffolds resolve this issue by offering quick repositioning and minimal setup. If a project requires time efficiency, it can be guaranteed through rolling scaffolding.
7. Versatile Applications
Another benefit of rolling scaffolding is that it is helpful for different applications and tasks such as plastering, painting, electrical work, construction, etc. Its mobility makes it a multi-purpose solution for indoor and outdoor tasks.
8. Improved Worker Safety
Rolling scaffolding features a stable platform, a non-slip surface, and other safety features to offer a safe working environment for workers. This scaffold allows workers to perform various tasks at elevated heights safely.
9. Locking Mechanisms
Another benefit of rolling scaffolds is their locking casters. Wheels can be fixed in place using brakes or locking wheels. The scaffold platform remains stable while workers are standing on it. This locking system maintains the overall safety of workers even when the scaffold is placed on a slightly uneven area.
10. Safe Platform
Mobile scaffolds offer workers a safe platform. Scaffold platforms can easily carry the weight of tools, workers, and materials. Their reinforced material and non-slip surfaces reduce the risk of incidents and offer workers peace of mind, as they can continue working on the task without worrying about balance or instability.
11. Frequent Position Changes
Another plus point of rolling scaffolds is that they allow frequent position changes. Workers can effortlessly relocate this scaffold to different job site areas through its wheels. This frequent relocation is quite useful for tasks like painting or maintenance, as workers need to adjust a scaffold at different angles and places multiple times.
12. Reduced Dismantling
The biggest advantage of working with rolling scaffolds is their reduced dismantling. Workers can save significant time, effort, and energy by setting them all up at once and then moving them around without dismantling them repeatedly. This reduced dismantling also reduces the risk of error or delay, which is familiar with frequent dismantling and reassembly of a traditional scaffold.
13. Reassembly
Another benefit of rolling scaffolds is eliminating the need for continuous reassembly. Once you set them up, you can move them around quickly without losing structural integrity. They save labour, time, and energy and allow you to work efficiently.
14. Increased Safety
Mobile scaffolds are designed with locking mechanisms, strong construction, and guardrails. These features reduce the risk of falls and injuries and increase the overall safety of workers in the work environment.
15. Versatility
Rolling scaffolds are versatile, as they are beneficial in various tasks, from construction to electrical work. They are adaptable to multiple job sites.
16. Efficiency
When it comes to increasing work efficiency, the mobility and ease of use features of rolling scaffolds allow workers to complete work on time. They spend less time assembling and dismantling the whole structure and more time on their work. Zero interruption streamlines their workflow and makes them more efficient in the work environment.
17. Space-Saving Design
A rolling scaffold has a compact design. You can find foldable mobile scaffolds or scaffolds with modular components. When it comes to storing a rolling scaffold, it takes less space, making it ideal for projects with limited space.
18. Cost-Effective in the Long Run
The biggest benefit of rolling scaffolds is that they’re a very cost-effective option in the long run. Although the initial investment in this structure is high, its durability and reusability offset the initial cost. The cost of repair or replacement is minimal over time. Its ease of use enhances worker productivity and reduces project timelines.
What Are the Types of Rolling Scaffolding?
The ten types of rolling scaffolding are as follows:
- Mobile Towers
- Genie Lifts
- Square Towers
- Baker style
- Perry style
- Narrow frame
- Modular type
- Fabricated frame
- Tube and coupler scaffolds
- Single bay scaffold tower
1. Mobile Towers
Mobile towers are common types of rolling scaffolds designed with wheels or castors that allow workers to move the scaffold quickly throughout the work environment. They come with an adjustable height option, so you can adjust the height per job requirements. They are lightweight and stable temporary structures.
2. Genie Lifts
Genie lifts feature powered lifting mechanisms. They are highly mobile scaffolds commonly used in commercial and industrial areas. Their mechanized lifting systems reduce manual effort and boost productivity. Genie lifts are suitable rolling scaffolds for elevated tasks.
3. Square Towers
The square tower features a square base to distribute weight evenly throughout the structure and thus boost its overall stability. Square towers prove useful for tasks that require access to multiple sides and a broad working area.
4. Baker Style
Baker-style scaffolding has a narrow frame that makes it easy to fit in tight spaces. This type of rolling scaffold is easy to assemble and highly portable, so it’s commonly used for home improvement projects such as painting, ceiling work, and drywall installation.
5. Perry Style
Perry-style mobile scaffolds have a broad platform and substantial weight capacity. Its design offers a good balance of stability and portability. This design is versatile and thus used for various indoor and outdoor projects, from simple maintenance to complex construction projects.
6. Narrow Frame
Narrow-frame scaffolds are super slim and compact and usually designed to work in tight spaces. They prove helpful for indoor tasks such as painting, wall repair, etc. The slender structure enhances the temporary structure’s overall maneuverability through hallways and doorways.
7. Modular Type
Modular mobile scaffolds comprise pre-engineered components. They can be assembled and disassembled quickly. They offer customization and let workers create scaffolds with varied configurations. They are an expensive type of mobile scaffold and are quite suitable for tasks that require specific shapes and levels. They are normally famous in industrial settings.
8. Fabricated Frame
Fabricated frame scaffolds are designed with prefabricated frames that are easy to assemble and feature high load-bearing capacity. They can accommodate heavy tools and materials. A fabricated frame is a highly durable type of mobile scaffold.
9. Tube and Coupler Scaffolds
Tube and coupler scaffolds are mobile scaffolds with an adjustable structure. Tubes and clamps allow workers to customize the scaffold’s design for different project sizes and shapes. They offer unmatched flexibility and strength, though their assembly requires more labor than other types of rolling scaffolds.
10. Single Bay Scaffold Tower
Single bat scaffold towers are the most common types of rolling scaffold. Their design features compact towers, which are usually created for small-scale tasks. They allow workers to complete tasks at moderate heights or in tight workspaces, and they are easy to assemble and transport.
What Are the Disadvantages of Rolling Scaffolding?
The disadvantages of rolling scaffolds are as follows:
- Limited stability on uneven surfaces
- Risk of tipping
- Weight capacity limits
- Frequent inspection needs
- Operational checks
- Structural failures
- Electric shocks
- Tip-overs
- Height Limitations
- Weight Restrictions
- Stability Concerns
- Surface Requirements
- Cost for Small Projects
- Maintenance Needs
1. Limited Stability on Uneven Surfaces
The most significant disadvantage of a rolling scaffold is its limited stability on uneven surfaces. They can’t be used on uneven ground. There is a risk of tilting and structure collapse with mobile scaffolds when used on uneven terrain. You must use a stabilizer or leveling jacks to roll a scaffold on a bumpy surface.
2. Risk of Tipping
Another drawback of mobile scaffolds is the risk of tipping. If you move the scaffold around with materials or roll on it, it may lose its balance. To prevent such tipping risks, you need to handle the scaffold carefully or lock its wheels.
3. Weight Capacity Limits
Another problem with rolling scaffolds is that they have lower weight capacity limits than traditional scaffolds. If you exceed the structure’s weight limit or overload it, its overall stability will be compromised. Therefore, mobile scaffolds should not be used for heavy-duty construction projects.
4 .Frequent Inspection Needs
Mobile scaffolds can easily be moved around frequently. This frequent movement requires careful inspection of wheels, locks, and joints to ensure safety. This inspection reduces the risk of structural failures and accidents because damage or technical issues can be resolved on time if there is any such issue.
5. Operational Checks
Rolling scaffolding requires operational checks on its platform, wheels, and other components. These checks are essential to ensure proper assembly, and failure to keep up with these regular checks will reduce workers’ safety and create a dangerous working environment.
6. Structural Failures
Mobile scaffolds remain in a mobile position over time. This continuous movement often weakens their structural parts. Wear and tear in locking casters, cracks, or bends in the frame lead to unexpected structural collapse. The best way to prevent structural failure is to do regular inspections so that parts can be repaired or replaced when the issue is identified on time.
7 .Electric Shocks
Another disadvantage of rolling scaffolding is the risk of electrical shocks if it gets close to live wires or electrical sources. Metal frames are part of mobile scaffolds. These metal frames can conduct electricity and put workers’ lives at risk. To prevent electric risks, non-conductive materials must be used in the scaffold structure, or a safe distance must be maintained.
8. Tip-Overs
Rolling scaffolding can tip over due to high winds or when used on uneven ground. There is a risk of tip-over, especially when you move the scaffold while the load is on the scaffold platform during movement.
9 .Height Limitations
According to OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines in the United States, rolling scaffolding must follow the 4:1 height-to-base ratio and an additional support system must be installed to create a taller structure. This height limitation makes it an impractical temporary structure for extreme heights, especially for high-rise buildings.
10. Weight Restrictions
Rolling scaffolding has weight restrictions that workers need to adhere to. Overloading this structure disrupts structural integrity and leads to injury or accidents.
11 . Stability Concerns
Rolling scaffolding lacks stability when it is mobile. Additional locking mechanisms or stability are needed to enhance safety in the work environment, especially when workers are completing tasks at elevated heights. Without such an addition, the whole structure may wobble.
12. Surface Requirements
The biggest issue with Supported scaffold sets is that they require flat surfaces on which to place them if you want the optimal level of stability and performance. You also need additional locking devices in the overall design in case you plan to use them on rough terrain. This limitation makes mobility scaffolds impractical for outdoor projects with uneven surfaces.
13. Cost for Small Projects
Another drawback of rolling scaffolding is its high cost for small-budget projects. You can rent ladders or small scaffolds instead, if you have a limited budget, However, its high rental cost makes it less economical for minor tasks.
14 .Maintenance Needs
Rolling scaffolds require frequent maintenance and repair. Careful inspection of its locking casters, locks, and other structural components is also necessary. Maintenance costs will increase over time if routine upkeep is overlooked,
What are the Uses of Rolling Scaffolding?
The uses of rolling scaffolding are as follows:
- Building Construction
- Maintenance and Repair Work
- Painting and Decorating
- Window Cleaning
- Electrical Installations
- Ceiling Repairs
- Tight or Narrow Spaces
- High-Rise Buildings
- Painting tasks
- Drywall installation
- HVAC installation
- Event setups
- Stage lighting
- Sound equipment and Rigging
- Manufacturing plants
- Industrial plants
1. Building Construction

Rolling scaffolds are used for various construction tasks, such as plastering, bricklaying, and installing exterior components. Their mobility and adjustable height features make them useful for various stages of construction, such as foundation work and finishing touches.
2. Maintenance and Repair Work

Mobile scaffolds are commonly used for repair and maintenance tasks. Workers can use this temporary structure to fix facade damage, replace tiles, repair a roof, etc. Mobile scaffolds offer ease of movement and reduce downtime.
3. Painting and Decorating

Rolling scaffolding is used to paint the walls, ceilings, and exteriors of buildings. Workers can reposition this temporary structure and cover large areas without repeatedly climbing up and down.
4. Window Cleaning

Mobile scaffolds are also helpful in window cleaning tasks. Whether workers clean residential or commercial building windows, this temporary structure proves helpful. Workers get easy access to hard-to-reach areas. Mobility lets the workers move across the facade while covering multiple windows simultaneously.
5. Electrical Installations

Rolling scaffolds are also used for electrical installations. Workers can install lighting fixtures, wires, and other electrical components at varied heights.
6. Ceiling Repairs

Mobile scaffolds prove quite helpful during ceiling repair tasks. Workers can effortlessly use rolling scaffolds to fix roof leaks, replace tiles, and install HVAC systems. They don’t need ladders, as mobile scaffolds provide a safe and stable working platform.
7. Tight or Narrow Spaces

Narrow-frame scaffolds are commonly used in tight and narrow spaces. The compact design of rolling scaffolds makes them useful for indoor use. They allow workers to work in tight areas without compromising safety.
8. High-Rise Buildings

Mobile scaffolds are also used to complete various tasks on high-rise buildings, such as painting, repair, or facade cleaning. Contractors use stabilizers or outriggers to provide additional support to this temporary structure at higher elevations.
9. Painting Tasks

Mobile scaffolding proves quite beneficial for large-scale painting projects. Painters can cover large areas such as high-rise walls, ceilings and tall exteriors through this temporary structure. It allows them to reposition the structure without any assembly. They only need to unlock its wheel and move it around. Painters can complete tasks with minimal fatigue and any interruption through mobile scaffolds.
10. Drywall Installation

Rolling scaffolds are used during the installation and repair of drywall. They offer workers a stable platform to handle and position large frames of drywall sheets. Since this scaffold has an adjustable height structure, workers can easily adjust its height to accommodate different ceiling and wall levels.
11. HVAC Installation

Rolling scaffolds are also helpful during the installation and maintenance of HVAC systems. They allow HVAC professionals to access ductwork, machinery, and vents at different elevations. Mobile scaffold platforms offer a stable and secure surface for workers to handle heavy tools and equipment.
12. Event Setups

Rolling scaffold is frequently used during event setup. It is used for backdrops and temporary structures at events. It is also helpful for setting up and dismantling event decor, signage, and temporary installations. Workers make the most of its quick repositioning during event preparation.
13. Stage Lighting

Mobile scaffolds help install and adjust lighting systems in concert venues and theatres. Electricians and technicians can use rolling scaffolds to work at different heights. This temporary structure provides them with a stable platform that they can use to install lights or adjust them with precision and ease. They can do this complete setup in less time with a mobile scaffold while quickly accessing different levels of buildings.
14. Sound Equipment and Rigging

Rolling scaffolds are also used to set up rigging equipment and a sound system at different events. Technicians can position speakers and cables at various points through mobile scaffolds. They can also adjust the height of the scaffold and perform technical setups with ease.
15. Manufacturing Plants

Rolling scaffolds are helpful during manufacturing facility assembly, repair, and maintenance. Technicians can access the factories’ industrial machinery and electrical systems through this temporary structure. Workers can quickly move between stations through mobile scaffolds, as it prevents the need for various setups.
16. Industrial Plants

Mobile scaffolds are commonly used for large-scale installation, inspection, and maintenance work in industrial plants. Workers can use rolling scaffolds to access machinery, high tanks, or other structural elements of industrial facilities.
What are the Parts of a Rolling Scaffold?
The twenty seven parts of the rolling scaffold are as follows:
- Base plates and casters
- Standards (uprights)
- Ledgers (horizontal beams)
- Transoms
- Diagonal braces
- Platforms and planking
- Guardrails and toeboards
- Lock scaffold wheels
- Outriggers
- Access ladders
- Locking casters
- Standards
- Ledgers
- Cross Braces
- Horizontal Braces
- Putlogs
- Rails/Guard Boards
- Volts
- Couplers
- Wheels/Casters
- Scaffold wheels
- Wheel Locks
- Swivel Locks
- Stabilizers
- Outrigger frames
- Vertical members
- Separate sections
1. Base Plates and Casters

Base plates are flat supports placed on the ground, and casters are wheels attached to the base of a rolling scaffold. Base plates enhance the stability of mobile scaffolds, and Casters let workers move the scaffold structure easily across the worksite.
2. Standards (Uprights)

Standards are vertical poles that create the main structural framework of mobile scaffolds. They transfer the scaffold’s weight and all the load it carries down to the base plates, useful for maintaining the vertical stability of a rolling scaffold.
3. Ledgers (Horizontal Beams)
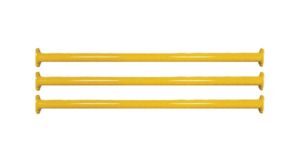
Ledgers are horizontal tubes that run parallel to the scaffold’s length and connect the standards. They serve as attachment points for other parts and planks. They provide lateral support to mobile scaffolds.
4. Transoms

Transoms are horizontal tubes set at a specific angle to the ledgers. They run across the width of the scaffold. Transoms enhance the rigidity of rolling scaffolds and distribute the load evenly throughout the structure.
5. Diagonal Braces

Diagonal braces are bars placed diagonally across the framework. They enhance structural integrity during movement and under lateral forces, preventing scaffolds from collapsing under heavy loads.
6. Platforms and Planking

Platforms are flat surfaces made of composite material, metal, or wood. They are a secure work area where workers can operate, hold tools, and store materials.
7. Guardrails and Toeboards

Guardrails are horizontal bars placed on the platform’s edges. They serve as protective barriers for workers and protect them from accidental steps off the platform. Toeboards are low barriers placed on the base of the platform. They prevent tools or equipment from falling off scaffolds.
8. Lock Scaffold Wheels

Lock scaffold wheels are castors designed with a locking mechanism. You can lock the wheels during operation to prevent accidental movement or rolling.
9. Outriggers

Outriggers are extendable supports attached to the scaffold’s base and used to widen the foundation. When rolling scaffolding is needed at elevated heights, outriggers are usually used to increase the structure’s stability and prevent tall temporary structures from tipping over.
10. Access Ladders

Access ladders are scaffold ladders that offer safe and easy access to different levels. They reduce the risk of falls or injuries, as workers can use secure ladders to climb onto platforms or move between scaffold platforms
11. Locking Casters

Locking casters are scaffold wheels with a locking feature. Once you turn on the lock, the mobile scaffold won’t move accidentally.
12. Cross Braces

Cross braces are diagonal parts of mobile scaffolds set in an “X” shape. They reinforce scaffolds, preventing them from swaying and collapsing under heavy wind or shifting loads. Cross braces distribute the load throughout the framework and ensure the structure remains rigid and straight during use.
13. Horizontal Braces

Horizontal braces are tubes placed parallel to the ground and connecting to the standards. They are installed at various levels to provide support to the scaffold platform or planks on which workers stand.
14. Putlogs

Putlogs are horizontal beams that run between the structure being worked on and the scaffold. They support the planks and board and distribute the load across the scaffold and its supported structure. Putlogs are an integral part of traditional scaffolds but are also used in rolling scaffolds when needed.
15. Rails/Guard Boards

Horizontal safety barriers, including top and mid rails, are installed at the platform edges. They ensure worker’s safety at heights. Guard rails or boards are essential safety features of mobile scaffolds as they reduce the risk of accidental slips or stepping off scaffold platforms.
16. Volts

Volts are fasteners used to connect different parts of the scaffold, such as standards, braces and ledgers.
17. Couplers

Couplers are clamps used to join scaffold tubes at different angles. They are fittings that connect scaffolding parts, such as braces, standards, and ledgers. They maintain structural integrity by holding the structural components of mobile scaffolds tightly together.
18. Wheels/Casters

Wheels or Casters are attached to the scaffold base, equipping the structure with swivel capability.
19. Scaffold Wheels

Scaffold wheels are casters designed to make rolling scaffolds mobile. They are durable and support the structure’s weight, workers, and tools. Rolling Scaffolds set on wheels allow workers to reposition the structure effortlessly.
20. Wheel Locks

Wheel locks are a locking mechanism that is integrated to scaffold wheels. Locks keep the mobile scaffold stationery when used and prevent accidental structure movement.
21. Swivel Locks

Swivel locks are locking mechanisms for the swivel feature of wheels. They ensure that wheels don’t rotate unexpectedly, allow precise positioning of the scaffold, and ensure the stability of the structure during use.
22 .Stabilizers

Stabilizers are support structures for rolling scaffolds. These components increase the stability and balance of the scaffolding structure. They work as a core foundation for the scaffold tower. They are made of highly durable aluminium tubes designed for heavy-duty use.
23. Outrigger Frames

Outrigger frames extend outward from a scaffolding frame and provide additional support and stability at the foundation of the rolling scaffold. Outrigger frames are essential, especially when a rolling scaffold structure is tall or narrow. These frames broaden the base and prevent the overturning of the structure. Outrigger frames are designed with adjustable legs or screw jacks that are crucial when you need to set up mobile scaffolds on uneven ground.
24. Vertical Members

Vertical members are upright tubes that serve as the backbone of a rolling scaffold. They provide the necessary height for workers to access elevated areas. These vertical members are made of strong materials and joined with horizontal members and ledgers to form a stable framework.
25. Separate Sections
The modular type of mobile scaffold uses separate sections that are connected to build a larger structure. This modular form of scaffold unlocks flexibility and makes the structure adaptable to different job specifications and site conditions. The best thing about separate sections of mobile scaffolds is that workers can dismantle and transport them easily.
How much is the rental of rolling scaffold in UAE?
The rent of a rolling scaffold in the UAE is around AED 1500-2000 per hour. The exact rental quote depends on the type and scaffold you need and also the location.
What Are The Safety Requirements of Rolling Scaffolding?
The thirteen safety requirements of rolling scaffolds are as follows:
- Proper surface
- Wheel locks
- Guardrails and Toeboards
- Height-to-Base Ratio
- Load Capacity
- Proper Assembly
- Regular inspections
- Stabilizer and Outriggers
- Avoid moving while Occupied
- Proper Training
- Electrical Safety
- Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Weather considerations
1. Proper Surface—Always use a rolling scaffold on flat and level surfaces. This temporary structure may tip over or become insatiable when used on uneven surfaces. If you plan to use them on uneven ground, you can use base plates or leveling jacks.
2. Wheel Locks- Another safety requirement for rolling scaffolding is to lock its wheels or caster. You need to make sure that locks are secure before workers.
3. Guardrails and Toeboards—Before you start using the scaffold, ensure that guardrails and toeboards are installed on the platform. These safety devices are essential for safety and prevent material, workers, or debris from falling off the scaffold.
4. Height-to-Base Ratio—The essential safety requirement of a rolling scaffold is its safe height-to-base width ratio, which must not exceed 4:1 unless you plan to use outriggers or stabilizers.
5. Load Capacity—When you want to use a rolling scaffold safely, make sure that you never overload it. Every mobile scaffold has a maximum load capacity, such as the weight of workers, tools, or material it can handle. Try to stay within its load capacity, as overloading may lead to structural collapse.
6. Proper Assembly—Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when assembling rolling scaffolds. Before using the structure, ensure every component is installed correctly and tightly secured.
7. Regular Inspections—Another crucial safety requirement for rolling scaffolds is to perform regular inspections. Continuous movement often leads to loose connections, damage to any structural component, and wear or tear. Regular inspection can identify damaged parts. Before each use, ensure the condition of the locks, wheels, braces, and platforms is good.
8. Stabilizers and Outriggers—You can use stabilizers or outriggers,if you want to increase the stability of a mobile scaffold at a higher elevation,
9. Avoid Moving While Occupied—Don’t move the scaffold when workers, materials, or tools are on it. Always clear the scaffold before repositioning to prevent accidents.
10. Proper Training—Ensure that workers are thoroughly trained before using mobile scaffolds. They must know everything about safety hazards, assembly, and adequate scaffold use.
11. Electrical Safety- One of the most significant safety requirements to follow while using a mobile scaffold is maintaining a safe distance of the structure from electrical sources or power lines. You can use non-conductive material, such as fiberglass, if you work near electricity.
12. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)—Workers should wear PPE while using mobile scaffolds. They can wear hard hats, gloves, a harness, non-slip shoes, or any other equipment necessary to perform a task safely.
13. Weather Considerations—Another safety requirement is not to use rolling scaffolds in heavy rain or high winds.
What are the OSHA Standards for Rolling Scaffolding?
OSHA Standards for Rolling Scaffolds define different safety standards due to their mobility functionality. If you use a mobile scaffold for projects, you must follow OSHA standards for workers’ fall protection. Regular inspections are required before, during, and after the use of rolling scaffolds. Common hazards alongside rolling scaffolds are tip-overs, falls from heights, structural failures, and electrical shocks.
Here are some OSHA safety guidelines that you need to follow for OSHA compliance:
- Immediately remove and replace them asap to prevent injury, death, or unfortunately, if you find any damaged parts during inspections.
- Always make sure that planks are fully secured.
- Brace rolling scaffold diagonally, crosswise, horizontally, or in a combination thereof to prevent the whole structure from racking or collapsing. This will secure the vertical members of the framework together and square and automatically align all vertical members.
- You need to plumb, level, or square a mobile scaffold.
- All brace connections must be fully secured.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions during scaffold assembly.
- Get easy access to the scaffold platform through built-in access ladders.
- Ensure brakes are present in every wheel or caster to prevent accidental swiveling or roll.
- Appropriate guardrails must be installed on the scaffold.
- Always follow the load capacity limit to maintain the structural integrity of a mobile scaffold.
- Increase the base dimension of the rolling scaffold with outrigger frames.
- Always push toward the base whenever you need to move a rolling scaffold.
- Every worker must have adequate training on how to use and erect these scaffolds.
- Ensure castor brakes are locked before climbing onto a rolling scaffold.
- Before moving the mobile scaffold, ensure you have removed all the equipment, personnel, and materials from the scaffold platform.
- Employees should be fully trained to use a fall arrest system if they need to use it on a rolling scaffold.
According to OSHA standard 29 CFR 1926.452(w)(6), the employee shouldn’t climb on the scaffold unless the following conditions are met:
- The surface on which a mobile scaffold needs to move must be within degrees of level and free of clutter, obstructions, holes, and pits.
- The height-to-base width ratio during movement is 2:1 or less, but there is an exception for a scaffold specially designed to meet and exceed nationally recognized stability test requirements.
- Whenever you plan to use outrigger frames, they must be installed on either side of the mobile scaffold.
- Propelling force must be applied directly on the wheels and shouldn’t produce a speed of more than 1 foot per second or 0.3mps if you employ a power system for mobile scaffolds.
- The contractor needs to ensure that no employee or any part of the scaffold extending outward should not be beyond the limit of casters, supports, or wheels.






